Products
Luoyang Judian Metal Hot Processing Equipment Co., LTD is mainly engaged in the manufacture of complete sets of equipment in the metal thermal processing industry and the integration of the entire production line.
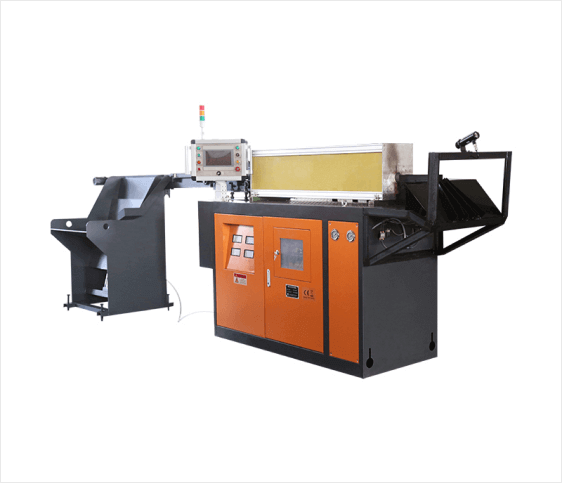

Induction Heating Furnace

Billets Heating Furnace

Steel Slab Heating Furnace

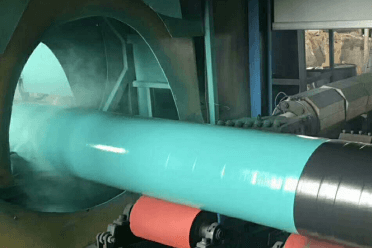
Large Steel Pipe Heating Furnace

Induction Steel Melting Furnace

Stainless Steel Melting Furnace

Aluminum Melting Furnace

Copper Melting Furnace

Zinc Melting Furnace

Gold Melting Furnace

Closed Cooling Tower

Aluminum Rod Horizontal Casting

Alu Rod Vertical Hot-top Casting

Alu Rod Continuous Casting and Rolling